Aspiration of Pleural Fluid
- Attach the 18-gauge over-the-needle catheter to a syringe and insert in the predetermined location
- Advance the needle slowly over the superior rib edge (along the anesthetized tract) to the predetermined depth while continuously pulling back on the plunger to maintain negative pressure in the syringe
- Once pleural fluid is aspirated, stop advancing the needle and carefully guide the catheter forward over the needle to the skin. Remove the needle from the catheter. You MUST COVER THE OPEN HUB OF THE CATHETER with a finger to prevent air entry into the pleural space
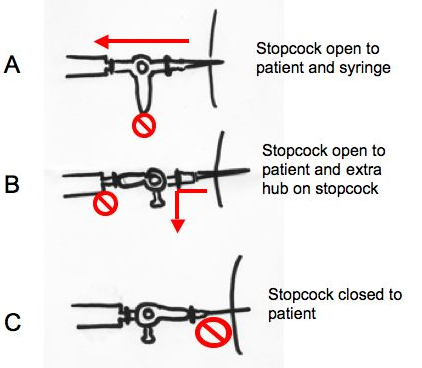
- Attach the large syringe fitted with the 3-way stopcock to the catheter hub. Ensure the stopcock is closed to the outside
- With the stopcock open to the patient and the syringe (figure A), aspirate 50mL of pleural fluid for diagnostic purposes and then close the stopcock to the patient (C)
- If more fluid is to be removed for therapeutic purposes, connect one end of the high-presure drainage tubing to the third limb of the 3-way stopcock. Attach an 18-gauge needle to the other end of the tubing, and insert this needle into the top of the large evacuated container. The stopcock should then be positioned so that it is open to the patient and the tubing, and closed to the syringe, so that fluid flows from the patient to the evacuated container.
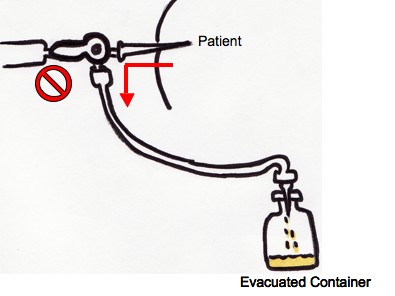
- When the procedure is completed, remove the catheter while the patient holds their breath at end expiration
- Cover the site with an occlusive dressing