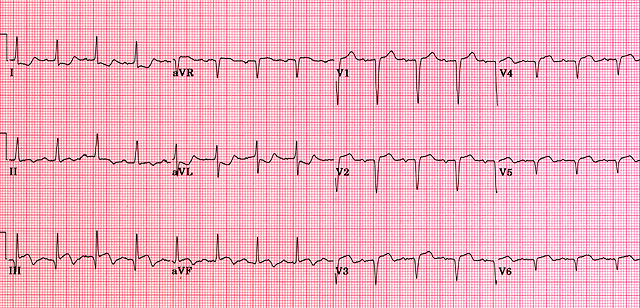
Acute right ventricular MI
In patients presenting with acute right ventricular MI, abnormalities in the standard 12 lead ECG are restricted to ST elevation greater than or equal to 1 mm in lead aVR. Although isolated right ventricular MI is usually seen in patients suffering from chronic lung disease together with right ventricular hypertrophy, it can occur in patients suffering a transmural infarction of the inferior-posterior wall which extends to involve the right ventricular wall as well. Right ventricular MI is most commonly caused by obstruction of the proximal right coronary artery and is frequently associated with right bundle branch block. Furthermore, only 5% - 10% of patients suffer from hemodynamic symptoms.