Port-A-Cath
Externalization of the Port
Recall that externalization of the Port-A-Cath for intermittent access refers to insertion of a non-coring needle luer-locked to extension tubing with a cap or saline lock.
Steps:
- Assess catheter site and surrounding skin. Observe for redness, swelling, tenderness or discharge at the portal site.
- Palpate dome. Cleanse portal site with chlorhexidine. Allow 60 seconds to dry.
- Cleanse portal site with normal saline to remove antiseptic.
- Dry area with 2x2 gauze.
- Prime capped access needle and extension tubing set with normal saline solution, then apply clamp on the extension device.
- Stabilize the dome between thumb and two fingers of one hand, in a tripod fashion.
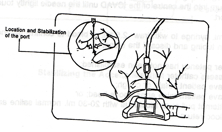
- At a 90-degree angle to the dome, push the access needle firmly through the skin and septum into the centre of the Port-A-Cath until the needle lightly touches the base of the port.
- Use a 10mL syringe to withdraw 2.5mL of blood to confirm patency. Discard (note- if using the Port-A-Cath for blood sampling, withdraw 10mL prior to obtaining sample to avoid contamination)
- If catheter patency is not established:
- Assess catheter for kinking
- Have patient inhale or cough
- Have patient raise arms above head, or
- Attempt pull-push technique with 20-30mL normal and attempt to confirm patency again
10. Connect IV tubing to the extension tubing and initiate infusion.
11. Apply a small amount of chlorhexidine ointment at needle entry site. Remove the access needle “wing” by pinching and lifting while immobilizing the needle
12. If there is a space between the patient’s skin and the bottom of the access needle platform, place a folded gauze underneath the platform to minimize needle movement.
13. Stabilize the needle by applying a transparent or gauze dressing.
Important Points to Remember:
- Secure all IV connections with luer lock and tape
- Never connect a syringe with a volume less than 10mL to a Port-A-Cath
- The average life of the septum is 1000-2000 penetrations with an access needle, however this depends on the gauge of the access needle, the size of the septum and the brand of the Port-A-Cath
- When administering multiple IV medications flush the line, extension tubing and access needle with a compatible solution. This reduces the risk of incompatible medication interactions