Pediatric Elbow Radiology
Step 2: Examine the fat pads
Evaluate the fat pads on the lateral flexed view. It is important that the view is a true lateral. It is important that the view is a true lateral. If note, abnormal fat pads can be missed.
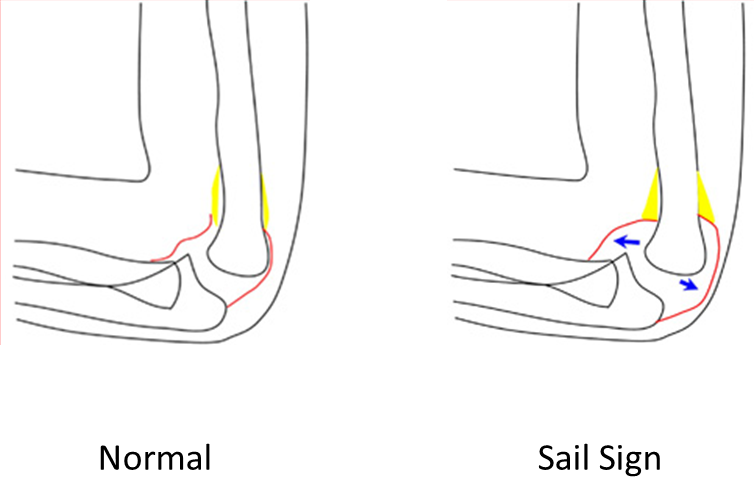
- The anterior fat pad is located in the coronoid fossa. A narrow anterior fat pad is a normal finding on the lateral view.
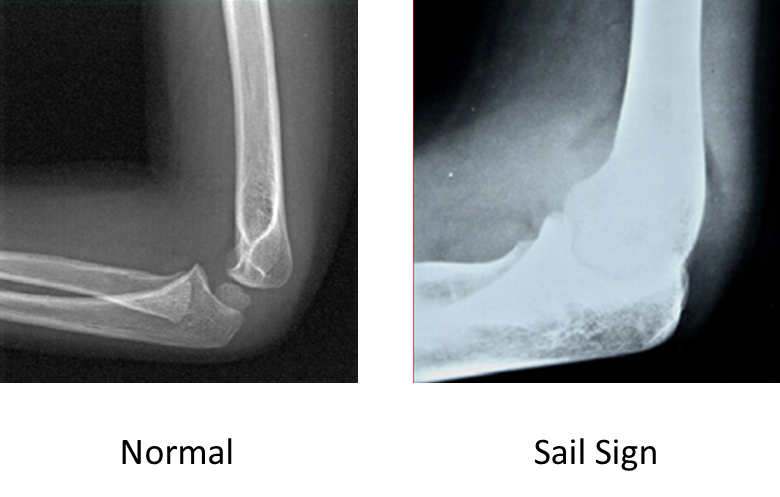
- The anterior fat pad can be displaced up and out by fluid in the elbow joint, creating the "sail sign". This usually indicates a fracture in children in the setting of an injury.
- The posterior fat pad is located in the olecranon fossa on the lateral view. It should not be visible under normal circumstances. Fluid in the elbow joint can displace the fat pad up and out making it visible on the lateral view. If the posterior fat pad is visible, it suggests a fracture in the setting of an injury.