Analysis and Interpretation of the Electrocardiogram
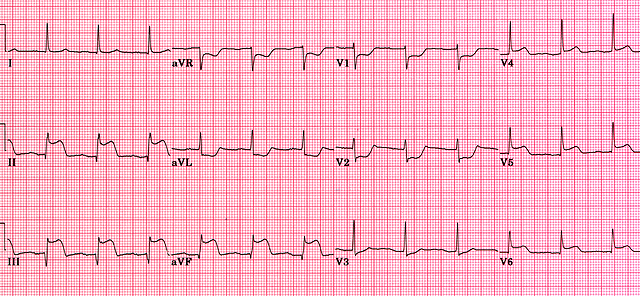
Acute posterior MI
When examining the ECG from a patient with a suspected posterior MI, it is important to remember that because the endocardial surface of the posterior wall faces the precordial leads, changes resulting from the infarction will be reversed on the ECG. Therefore, ST segments in leads overlying the posterior region of the heart (V1 and V2) are initially horizontally depressed. As the infarction evolves, lead V1 demonstrates an R wave (which in fact represents a Q wave in reverse). Note that the patient below is also suffering from an inferior wall myocardial infarction as evidenced by ST elevation in leads II, III and aVF.