Analysis and Interpretation of the Electrocardiogram
Step 3a: Calculate the electrical axis
The mean QRS axis refers to the average orientation of the heart's electrical activity. In most cases, an approximation of the axis will be sufficient for the ECG interpretation. There are many different approaches to axis determination, but this discussion will be limited to a simple technique which uses the leads I and aVF to calculate an approximate axis.
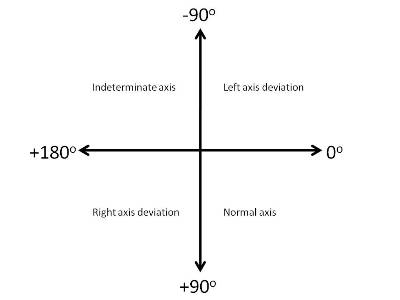
- Recall that the axis can be considered in terms of four quadrants, with lead I oriented at 0°, and aVF oriented at +90°. An ECG with the QRS axis oriented to the quadrant between 0° and 90° is said to be normal.
- An ECG with the QRS axis oriented to the quadrant between -1° and -90° is said to have left axis deviation.
- An ECG with the QRS oriented to the quadrant between +91° and 180° is said to have right axis deviation.
- An ECG with the QRS oriented to the quadrant between -91° and -180° is said to have an indeterminate axis because one cannot tell if it represents right or left axis deviation.