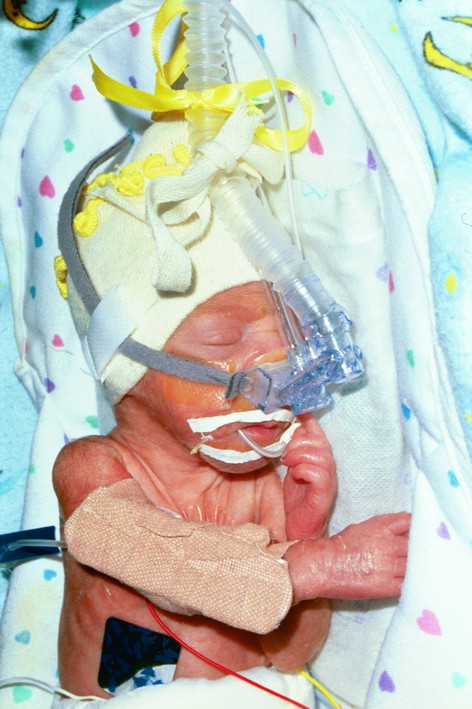
PT 861 - The High Risk Infant
Benefits of the different nesting positions
- Nesting in sidelying assists infants in maintaining hands together and lower extremities flexed, and encourages trunk flexion. This position also provides some support to the rib cage to facilitate respiration. It is important to make sure that the infant is positioned frequently on alternate sides to prevent plagiocephaly.
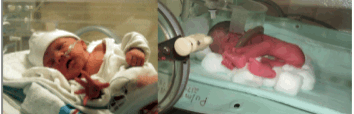
- In the sidelying position, approximation can be used to increase proprioception through the limbs, shoulder girdle and pelvis. In addition, weight-shifting sensory experience can also be easily provided.
- Nesting in prone provides maximal support to the chest wall; this support anchors the respiratory muscles and part of the rib cage, easing the work of breathing. Prone position also stimulates the development of postural muscles and head control. This position, however, is best tolerated in infants after 34 weeks of gestation, when they are able to lift and turn their head against gravity.
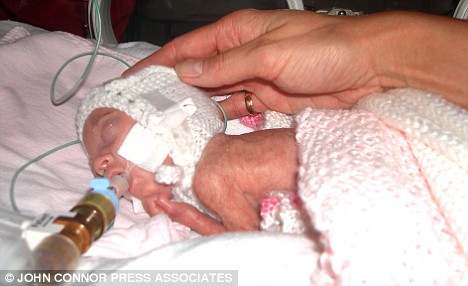
- Nesting in supine is indicated for fragile infants, allowing observation of the face and next.